Status Quo & Prospects of Southeast Asian paper, packaging and printing industries
Status Quo & Prospects of Southeast Asian Paper Industry – Speech Overview
Yuanzhe Consulting delivered a keynote speech on The Current Situation and Future Prospects of Papermaking, Packaging, and Printing Industry in Southeast Asia at the 19th Guangzhou International Paper Exhibition in 2024. The speech covered a comprehensive overview of the Southeast Asian paper industry, emphasizing its current status and future potential. It provided insights into the growth drivers, market trends, and challenges faced by the industry. The presentation also highlighted the emerging opportunities and technological advancements that are expected to shape the future of the paper industry in Southeast Asia.

The speaker is Dai Yuanfeng, partner (managing director) of Shanghai Yuanzhe Information Consulting Co., Ltd. We would like to thank the Guangdong Paper Industry Association and Guangzhou Aochi Exhibition Service Co., Ltd. for their help and support, as well as all the guests and friends present at the event for their strong support!

Yuanzhe Consulting’s booth A65 at the Guangzhou International Paper Exhibition
This time, Yuanzhe Consulting sent three staff members to participate in the Guangzhou International Paper Exhibition, namely Xiaoyue, Xiaoci and Hans (from left to right).

On the first day of the exhibition, many friends from all over the country came to Yuanzhe Consulting’s A65 booth to consult about Chinese companies’ overseas expansion and the economic and policy environment in Southeast Asia.


Southeast Asian paper, packaging and printing industries
Southeast Asia (SEA) is located in the southeast of Asia and consists of several countries and regions south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. Southeast Asia includes 11 countries, namely Brunei, Cambodia , Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand , Vietnam and East Timor. Except for East Timor, 10 countries in the region form the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN, abbreviated as “ASEAN”, “ASEAN” or “ASEAN” in Chinese). The total area of Southeast Asia is about 4.5 million square kilometers, with a total population of nearly 700 million.
According to Yuanzhe Consulting’s analysis, the economic levels of Southeast Asian countries vary greatly:
- Singapore has a developed economy and is the only developed country in Southeast Asia. Its economic activities are mainly based on the service industry, finance, shipping, logistics and tourism. In recent years, it has actively developed high-tech industries and education.
- The economic development levels of Malaysia and Thailand are among the highest in Asia. Their economies are mainly based on industry, manufacturing, tourism and agriculture. In recent years, they have actively developed advanced manufacturing, finance and logistics industries.
- The GDP per capita of the Philippines, Indonesia and Vietnam is relatively low, and they focus on basic manufacturing, agriculture, fisheries , tourism, etc., and export a large number of workers. Filipinos mainly go to the oil-producing countries in the Middle East, Japan, Hong Kong and Taiwan in East Asia, and Italy in Europe to work. Indonesians mainly go to Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong and the oil-producing countries in the Middle East to work. Vietnamese mainly go to East Asia to work.
- Myanmar, Cambodia , Laos and East Timor are underdeveloped countries. The economies of Myanmar, Cambodia and Laos are mainly based on tourism and agriculture, and the manufacturing industry is in its infancy; the economy of East Timor is only based on fisheries and oil exports.
- Although Brunei has a high GDP per capita and its industries are mainly based on the export of oil and natural gas, its wealth is concentrated in a small number of wealthy classes, just like the oil-producing countries in the Middle East, and its total economic volume is relatively low.
- Due to the lack of statistical data on East Timor and its extremely low economic output, in Yuanzhe Consulting’s Southeast Asia research series of reports, the concept of Southeast Asia is consistent with that of the ten ASEAN countries, and East Timor is not studied.

Overview of Southeast Asian Paper Industry
Southeast Asian countries such as Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam have rich forest resources, providing sufficient raw materials for the paper industry. Indonesia is particularly famous for its vast tropical rainforests and fast-growing eucalyptus and rubber tree plantations, making it an important global pulp and paper production base.
In terms of demand, the rapid economic growth and population increase in Southeast Asia have brought strong demand for paper, packaging and printing. This demand comes not only from the increase in domestic consumption, but also from the region’s position as a global manufacturing center, and the demand for packaging paper and industrial paper continues to rise. With the popularity of e-commerce, the development of the packaging industry has further promoted the demand for various paper, packaging and printing. In recent years, China’s papermaking \pulp and paper companies have expanded their overseas business in Malaysia, Vietnam and other countries, established factories, and further driven local related demand.
Although the overall technology and equipment level of the Southeast Asian papermaking industry may not be as good as that of developed regions such as North America and Europe, in recent years, many companies have begun to introduce advanced production equipment and technology to improve production efficiency and product quality. For example, some papermaking companies in Vietnam and Thailand have begun to adopt modern production lines and environmental protection technologies to meet the needs of the international market. Malaysia’s application of Industry 4.0 related technologies in the papermaking industry has enabled Malaysia’s papermaking industry to be further developed through modern production technologies.
As global environmental awareness increases, the Southeast Asian papermaking industry is also gradually transforming towards sustainable development. Many companies are beginning to adopt renewable raw materials and circular economy models to reduce environmental impact. For example, papermaking companies in Malaysia and Thailand are actively promoting forest certification programs to ensure sustainable sources of raw materials and reduce carbon emissions and water consumption during production.
Outlook for Southeast Asian Paper Industry
In the future, there is also a lot of room for the paper industry in Southeast Asia to develop. Driven by economic development, growing demand for all types of paper, and strategic investments by large global companies, the Southeast Asian paper industry will achieve substantial growth in the next few years and usher in a period of sustained growth. Indonesia, with its large population and rich forest resources, remains an important market. The country is expected to continue to be a major center for paper production and exports. Vietnam has attracted a large amount of foreign investment and is rapidly expanding its papermaking capacity. Vietnam’s strategic location and continuously improving infrastructure make it an ideal destination for paper companies. Malaysia’s paper industry benefits from both domestic demand and its strategic position as a gateway to other markets in Southeast Asia. The country’s recent investments are aimed at significantly increasing production capacity.
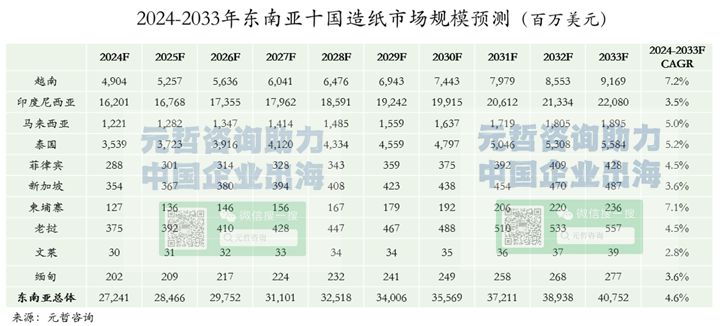
According to Yuanzhe Consulting’s forecast, the total papermaking market size of the ten Southeast Asian countries will be approximately US$40.752 billion in 2033. Among them, Indonesia, as the country with the largest economy in Southeast Asia, also ranks first among Southeast Asian countries in terms of papermaking market size, reaching US$22.08 billion, and it has an absolute leading position in Southeast Asia. Vietnam and Thailand rank second and third, with market sizes of US$9.169 billion and US$5.584 billion respectively in 2033. In terms of growth rate, Vietnam, Cambodia and Thailand rank among the top in Southeast Asia in terms of compound annual growth rate during 2024-2033.
Suggestions for Chinese companies entering the Southeast Asian market
- Through various channels, including the collection of secondary data and on-site market research, we can gain an in-depth understanding of the local market status, the market share of major competitors, the supply chain of local related products, etc. Yuanzhe Consulting Hanoi Office will do its best to help you better understand the Southeast Asian market.
- Understand local policies and laws, as well as the relevant policies issued by the Chinese government on overseas investment, and abide by legal red lines.
- Understand the local operating costs and operating models of similar foreign-funded enterprises
- Explore local demand points, start from the demand, and clarify your own positioning.
- Find suitable partners, such as local distributors and direct customers, when appropriate.
- By establishing a local office, you can initially test the local market by exporting your products.
- If there are many local orders, you can consider building a factory locally.
Yuanzhe Consulting helps you better understand Vietnam and other Southeast Asian countries, as well as overseas markets such as Mexico:
One-stop service: From assisting you in applying for a visa, arranging a trip to inspect factories and land in Vietnam, to negotiating with Vietnamese landlords, Yuanzhe Consulting provides one-stop service to ensure that your company can start and operate in Vietnam without worries. From the moment you decide to cooperate with Yuanzhe Consulting, you can arrive in Vietnam to inspect factories and land in about a week at the earliest.

